Charge: There are two charges in nature i.e., positive and negative. The negative
charge is due to electron. Its value is 1.6 x 10-19C. It is measured in coulombs.
Coulomb: One coulomb is the amount of charge present on 6.25 x 1018 electrons.
Electric Current: It is the rate of flow of charge through a conductor. If a net
charge Q flows across any cross-section of conductor in time t, then the current I,
through the cross-section is
The unit of current is ampere.
One Ampere: One ampere is constituted by the flow of one coulomb of charge
per second.
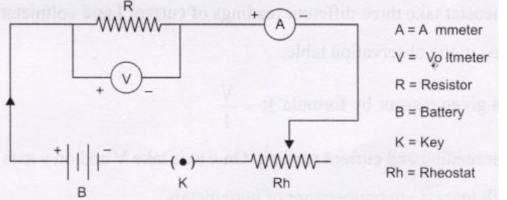
It is measured by a device called ammeter which is always connected in series in
a circuit.
Potential difference In an electric circuit carrying current, the work done to move a
unit charge from one point to the other is called potential difference.
The SI unit of potential difference is volt (V).
One Volt: When 1 joule of work is done to move a charge of 1 Coulomb from one
point to the other then potential difference is of 1 volt.
It is measured by an instrument called the voltmeter. The voltmeter is always
connected in parallel in a circuit.
e.m.f.: Electro motive force, is the force which disturbs the equilibrium of free
electrons flowing in the metal wire. The source of e.m.f. like cell or battery can
develop a potential difference across the ends of the wire and the electrons can
flow through the wire.
Ammeter: The number of electrons flowing through a wire can be measured using
ammeter. It is always connected in series in the circuit. The positive electrode of
battery/cell is connected to the positive electrode of the ammeter and the negative
end to the negative electrode of the battery.
Cell: A cell is a device which produces potential difference in the wire and
supplies the electrons to flow through the closed circuit. A primary cell produces
1.5 volts of potential difference.
Types of cells:
(a) Primary cell like dry cell, Lechlanche cell is used in torch, transistors etc. It
produces 1.5 volts of p.d. (potential difference). For effective use should be used
intermittently.
(b) Secondary cells can be recharged using a charger. The cell is connected to the
charger and the electrons are stored in it which can be used later. Such cells are also
called accumulators or storage cells
Ohm’s law: The current flowing through a metallic conductor held at constant
temperature is directly proportional to the potential difference between the ends.
V = IR
Resistor: It is an electric wire which offers resistance to the flow of current
through it. Its unit is Ohm (Ω).
Resistance: When the electrons flow through a wire, they collide with the atoms
of the wire, due to this collision the speed of electrons flowing gets disturbed and
they also lose the energy in the form of heat energy. This obstruction for the flow
of electrons is called resistance.
Each and every wire that may be a very good conductor of electricity will certainly
offer some resistance to the flow of electrons
Factors affecting resistance:
(a) If the wire is long then the collision of electrons flowing through the wire will be
more and hence it will offer more resistance. But if the wire is thick the collisions
would be less and the resistance offer would be less. Hence, the resistance of the
wire depends on the thickness, length material and the temperature of the wire.
(b) If the wire is made up of same material and is thick the resistance will be less
as compared the long wire of
the same material at the constant temperature.
(c) This law is not valid for semiconductors like diode, thermistor, diode, filament
of lamp, light dependent resistor, LED etc. Therefore, all semiconductors are
called non-ohmic materials. cbse lab manual in science class 10 physics solutions, ohm’s law

Validity of Ohm’s Law: Ohm’s law is valid only under the condition when
temperature is kept constant. This is reasonable because when temperature is
constant only then resistance will be constant.
Galvanometer: It is an instrument used to measure very less current. cbse lab manual in science class 10 physics solutions, ohm’s law
Ammeter: It is an instrument used for measuring the magnitude of current flowing
through a circuit. It is always connected in series, it offers very low resistance. It’s
unit is ampere (A).
Voltmeter: It is an instrument used for measuring the potential difference between
any two points of a given conductor. It is always connected in parallel in the circuit.
The unit is volts (V).
Rheostat: A component used to regulate the electric current flowing through a
circuit without changing the voltage is called Rheostat. It has variable resistance. It
is used to change the resistance in the circuit.